A sitemap or sitemap.xml is a specific XML file located at the root of an Internet resource. Many webmasters ask themselves the question: “Do I need to install a sitemap.xml on my website, and what effect does it have on the promotion of the site in search engines? Or is it not necessary to add a sitemap at all? "
In order to answer all these questions, we will analyze the sitemap structure and try to answer what this document is for.
Sitemap.xml is a list of all web pages on your site in xml format. The presence of this file allows search engines to significantly speed up the indexing of pages, but it is not a prerequisite for creating and promoting a site! It's just that in the absence of a sitemap, pages may not be included in the search engine index for a long time, especially if there are a lot of them or the portal has a deep nesting level.
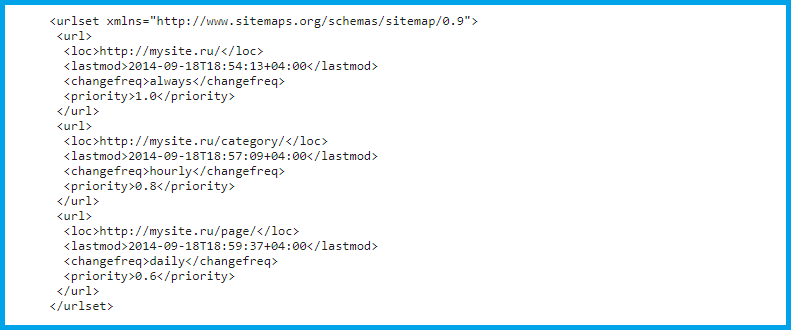
Only those pages should be added to sitemap.xml, which, in your opinion, should be in the index of search engines. Do not include pages that are not indexed in robots.txt, with dynamic URLs, authorization pages, profiles, and other technical web pages. The server header returned by all documents in the sitemap.xml file must be 200.
If your site has more than 10,000 pages, then you should make several sitemaps. The fact is that the maximum allowable sitemap.xml size is 10 MB, although Search Console, for example, allows you to add a sitemap with a maximum size of 50 MB.
At the very beginning, you need to specify the xml version and the encoding used, namely UTF-8.
Required tags:
"Urlset" - this tag opens at the beginning of your map (the tag is paired, respectively, it should be closed at the end of the document);
“Url” is a paired tag that is the main tag for every hyperlink in your document;
“Loc” is a paired tag containing a link to the page.
Optional tags:
“Lastmod” - shows the date when changes were last made to the document;
“Changefreq” indicates how often changes to the document are planned (approximately);
“Priority” - displays the priority of page scanning, takes values from 0 to 1.
Note! The “priority” tag is no longer supported by the Google search engine.
In the case where there are several sitemap.xml files (there are more than 10,000 pages on the site), the following tags are used:
“Sitemapindex” — this tag opens at the very beginning of your map (the tag is paired, respectively, it should be closed at the end of the document);
“sitemap” — is a paired tag, it is the main one for every hyperlink in the document;
“loc” — is a paired tag that contains a hyperlink to sitemap.xml;
“lastmod” — is an optional tag indicating the date when the web page was last modified.
To create a sitemap, you can use special services - automatic generators, for example:
1. Mysitemapgenerator.com. In the free version, it allows you to scan up to 500 pages, which is ideal for small portals. Using the paid packages ($ 2.5 and $ 4), you can index from 1 million pages to an unlimited number, setting up a sitemap update on a schedule (useful for portals where new web pages often appear).
(1).png)
2. Gensitemap.ru. Here you can scan up to 1000 pages for free. Paid packages vary depending on the number of pages you need to add to your sitemap.
.png)

If your website is developed on any of the common CMS, for example WordPress, then you can use any of the existing plugins - you do not need to use third-party services.
There are a huge number of plugins that generate a sitemap, for example, Google XML Sitemaps, WP Realtime Sitemap.
First, identify those pages on your website that you think are useful to users and should be added to the search engine index. You should also define canonical URLs for the selected web pages.
Choose the most suitable type of sitemap and create it using a third-party service or plugin.
Enter the link to the sitemap in robots.txt and add it to the webmaster's Google panel.
Google works with the following extensions:
XML;
RSS;
TXT;
HTML.
Regardless of the type of sitemap, it will have the following restrictions:
sitemap cannot include more than 50,000 URLs;
the file size cannot be larger than 50 MB.
If, when composing your sitemap.xml, you see that the file weighs more than 50 MB, you need to create 2 or more sitemaps. It is quite simple to do this:
Develop an index sitemap.
In your sitemap index file, include links to all of your other sitemaps.
Add the sitemap index document to the Search Console.
To add a sitemap to Search Console, in the Index section, select the Sitemaps tab and add the address of the map. Then your Sitemap will be scanned for errors, and the results will be displayed in the table below.
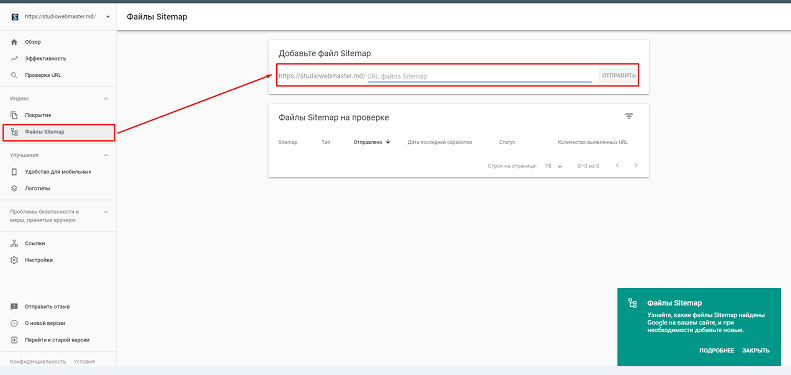
In the case of the Yandex webmaster, the procedure is the same (shown in the screenshot). You just need to insert a link to the map - and you're done.
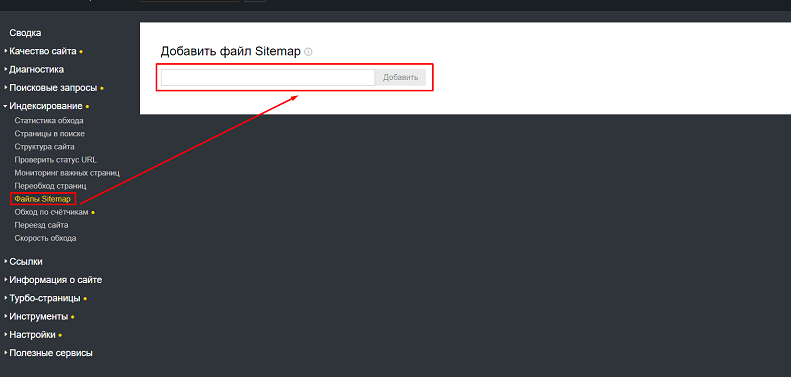
Before adding the file, you can check for errors. To do this, select the “Tools” section, then “Sitemap file analysis”.
broken links to a file (URL gives a 404 error);
web documents with 301, 302 redirects;
web pages with dynamic url.
Sitemap.xml really speeds up the indexing of web pages, which can be useful for multi-page sites like online stores. To get this file into the hands of Yandex or Google as soon as possible, you need to add it to the panels for webmasters.
It is not worth creating a map manually, because at the same time there is a high risk of typos and all kinds of errors, while free generators and plugins work according to an established algorithm.
For some Internet portals, sitemap.xml is simply not needed, so the rationality of creating and adding this file is determined by a SEO specialist after a detailed analysis of your portal. If you are independently engaged in compiling the structure of the site, we recommend reading an article about what is the usability of the site.
Leaders in the IT market |
| 14+ years of experience and innovative solutions to help your business stand out and grow. |
Inspiring portfolio |
| 150+ successful projects: from sleek landing pages to complex corporate systems. |
Team of experts |
| 51+ professionals who bring your ideas to life with maximum efficiency. |

| NOTORIUM TRADEMARK AWARDS |
| Notorium Trophy 2017, Notorium Gold Medal 2018, Notorium Gold Medal 2019 |

| TRADE MARK OF THE YEAR |
| Gold Medal 2016, Gold Medal 2017, Gold Medal 2018, Gold Medal 2019 |

| THE BEST EMPLOYER OF THE YEAR |
| According to the annual Survey conducted by AXA Management Consulting - 2017, 2018, 2019 |